Components of a CGM System
-
Sensor
Small, flexible, and disposable device that is inserted under the
skin to measure glucose levels in the interstitial fluid. -
Transmitter
Small device that is attached to the sensor. It wirelessly communicates with the sensor to receive the glucose data
-
Receiver/Smartphone App
Acts as the interface for the CGM system, allowing users to access real-time glucose data and make informed decisions.
-
Cover Tape
Specialized adhesive tape that safeguards and preserves
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) devices.
Advantages of CGM patches
A Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) system consists of four main components: the sensor, transmitter, receiver/smartphone app, and cover tape.
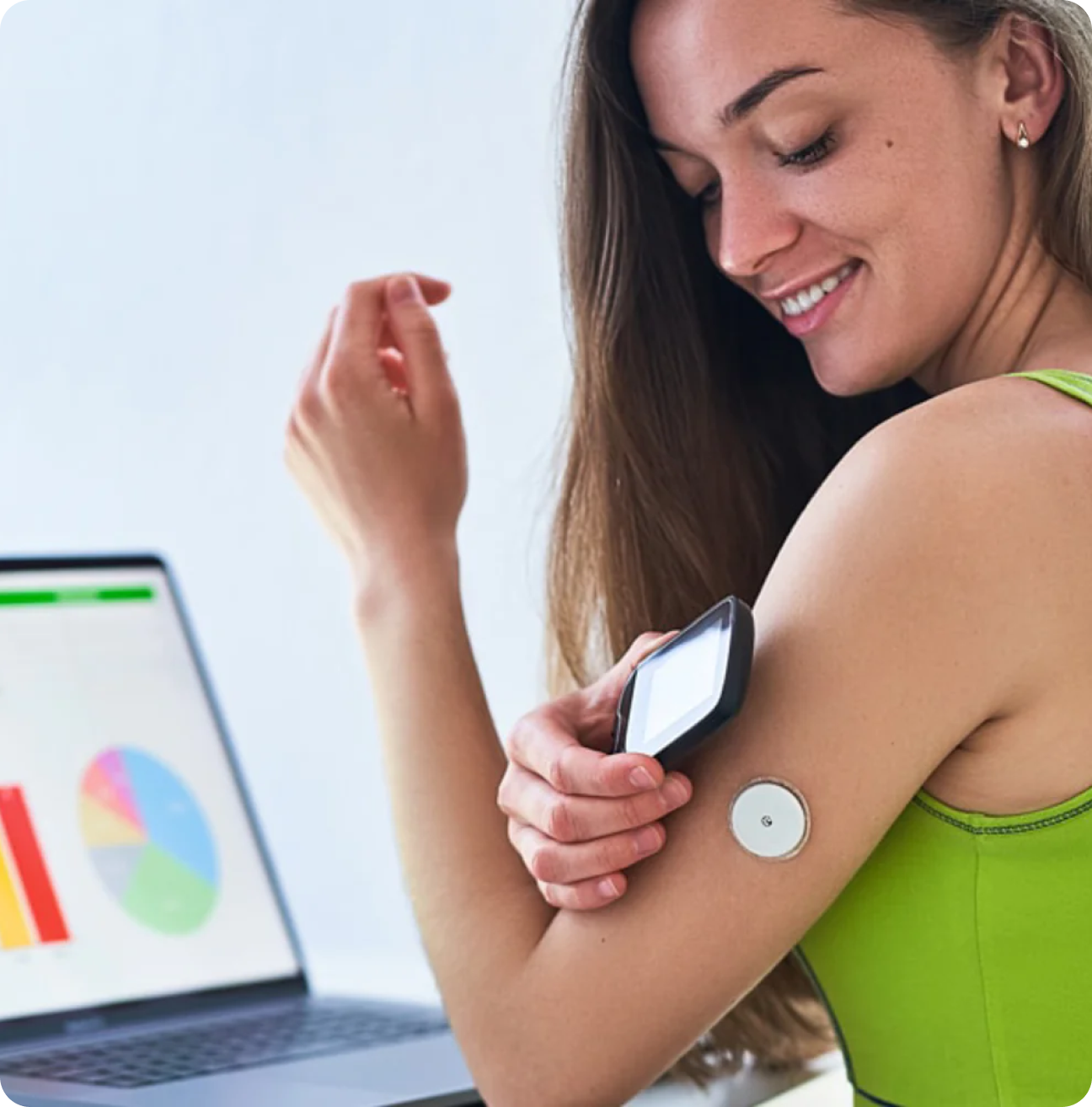

Early Detection of Glucose Patterns and Trends
CGM sensors provide valuable insights into glucose patterns and trends that would otherwise go unnoticed. By tracking glucose levels continuously, users can identify high or low blood sugar patterns, detect sudden spikes or drops, and recognize how their glucose levels respond to various factors such as meals, exercise, and stress. This early detection allows for prompt intervention and adjustment of treatment plans, minimizing the risk of hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia.
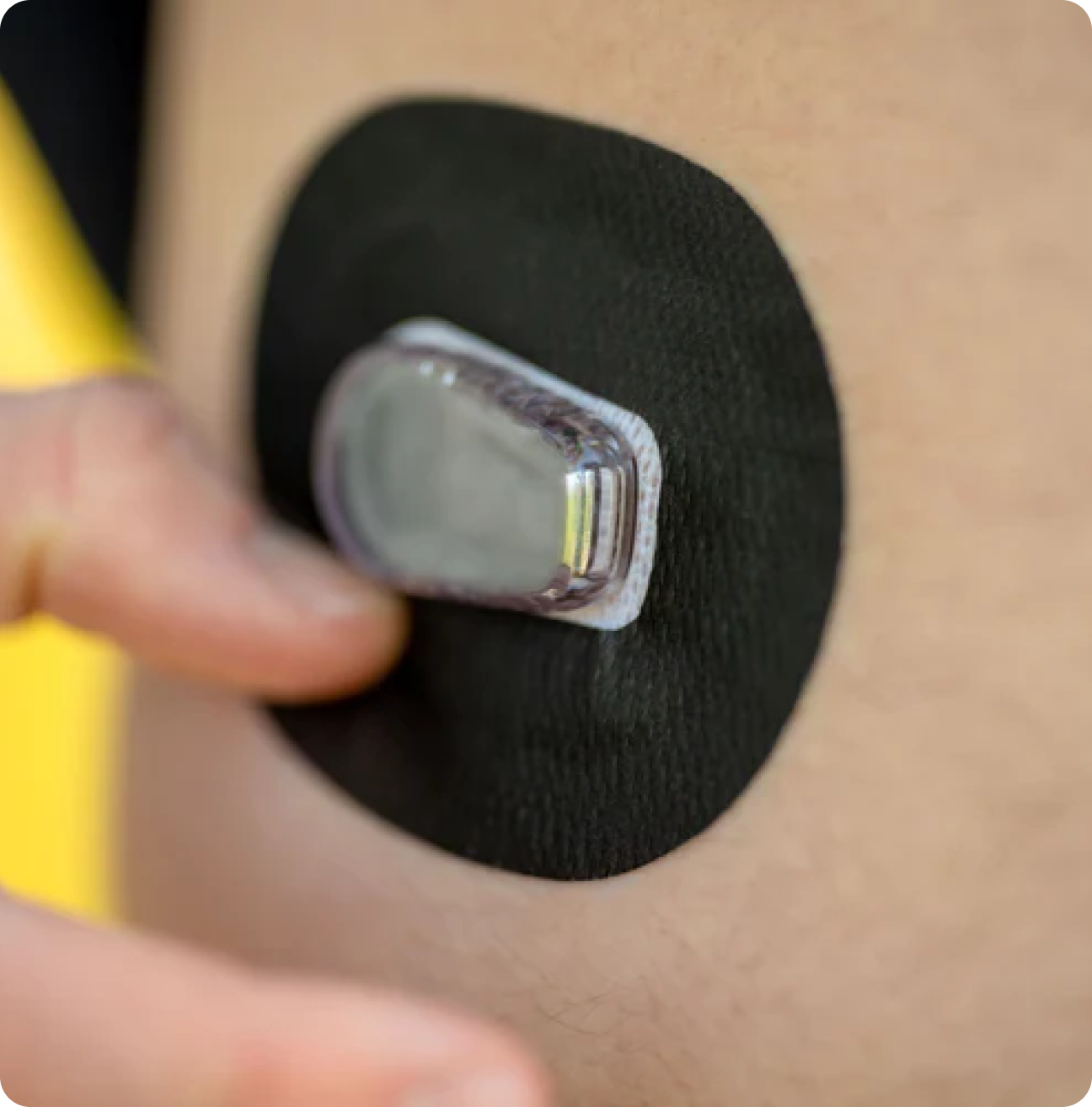
Alerts and Alarms for Improved Safety
- CGM sensors are equipped with customizable alerts and alarms that notify users when their glucose levels are approaching dangerous highs or lows. These alerts serve as life-saving tools, preventing severe hypoglycemic or hyperglycemic episodes.
- CGM technology and the use of CGM patches have transformed the landscape of diabetes management. Real-time data, early detection of glucose patterns, and customizable alerts empower individuals with diabetes to make informed decisions and take control of their health.
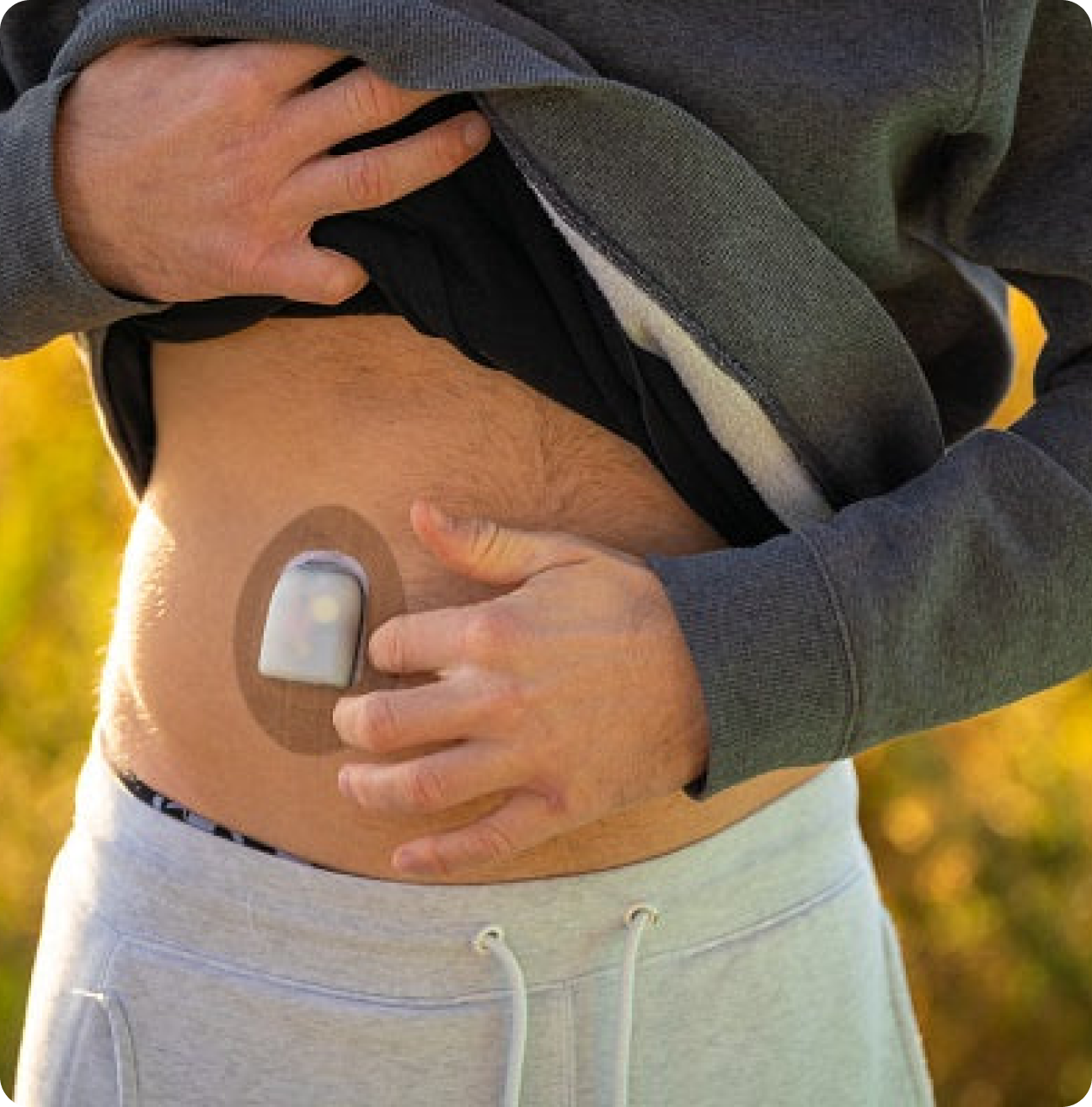
The Longest Lasting CGM Overlay Cover Tape is here
10-14 Days Of Staying Power Per Patch, 4-way stretch, and Non-Fraying. The longest-lasting patch on the market! Designed by Engineers.
Overlay designs for every popular device
Selecting the Right CGM Device
When choosing a Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) device, there are several important factors to consider.
Accuracy:
Choose a CGM device with a proven track record of accuracy, indicated by a low Mean Absolute Relative Difference (MARD) value.
Ease of Use:
Look for a user-friendly device with intuitive interfaces, easy sensor insertion, and clear glucose readings for convenient diabetes management.
Compatibility:
Ensure the CGM device can integrate with other devices or systems you use, such as insulin pumps or smartphone apps, for streamlined data tracking.

Wearability and Comfort:
Assess the size, weight, flexibility, and adhesive quality of the device to ensure comfort and secure attachment without irritation.
Data Accessibility:
Consider how easily you can access glucose data, whether through dedicated receivers, smartphone synchronization, or real-time readings and customizable alerts.
Cost:
Evaluate the initial device cost, ongoing expenses for sensors/transmitters, and additional fees for accessories or data services.
Support and Customer Service:
Look for reliable customer support channels, educational resources, and troubleshooting assistance from the manufacturer or supplier.
The Longest Lasting CGM Overlay Cover Tape is here
-
1. Proper sensor placement and application techniques
- Choose the right body areas:
- Prepare the site
- Inserting the sensor
- Placing the sensor
- Adhesive techniques for longevity
-
2. Maintaining CGM sensors
- Proper cleaning
- Protect from water damage
- Enhancing adhesion and stability with Plus Patches
- Ensure consistent adhesion and stability
By following these best practices and utilizing Plus Patches, you can maintain your CGM sensors effectively.
Understanding Glucose Readings and Trends
-
Glucose Readings on CGM Devices
- Current glucose level
- Trend arrows
- Historical data
- Target glucose range
-
Importance of Staying within the Target Glucose Range
- Diabetes management
- Symptom management
- Optimal functioning
- Long-term health outcomes
-
Interpreting Glucose Trends and Patterns on CGM Graphs
- Pre-meal glucose levels
- Post-meal glucose levels
- Exercise impact
- Medication effects
- Stress and emotional impact
- Time of day patterns
-
Working with Your Healthcare Provider
- Collaborate with your healthcare provider
- Make necessary adjustments to your treatment plan
- Regularly review CGM graphs
Overcoming Challenges with CGM Patches
Managing challenges related to physical activities, showering, and sensor wear during sleep is important to ensure accurate data from your CGM device. Here are some strategies to help you navigate these scenarios while keeping your sensors protected with the help of Plus Patches:

Physical activities:
Secure your sensor with Plus Patches:
Apply a patch over the sensor site to prevent dislodgement or damage during physical activities.
Consider sensor placement:
Choose a location that is less likely to be affected by friction or pressure from movement or equipment.
Stay hydrated:
Monitor your hydration levels and drink plenty of water before, during, and after physical activities to maintain stable glucose levels.

Showering and water-related activities:
Protect the sensor with a waterproof cover:
Use a waterproof cover or a waterproof adhesive patch, like Plus Patches, to shield the sensor from water during showering or swimming.
Follow manufacturer guidelines:
Adhere to the guidelines provided by your CGM device manufacturer regarding water exposure to maintain device integrity.
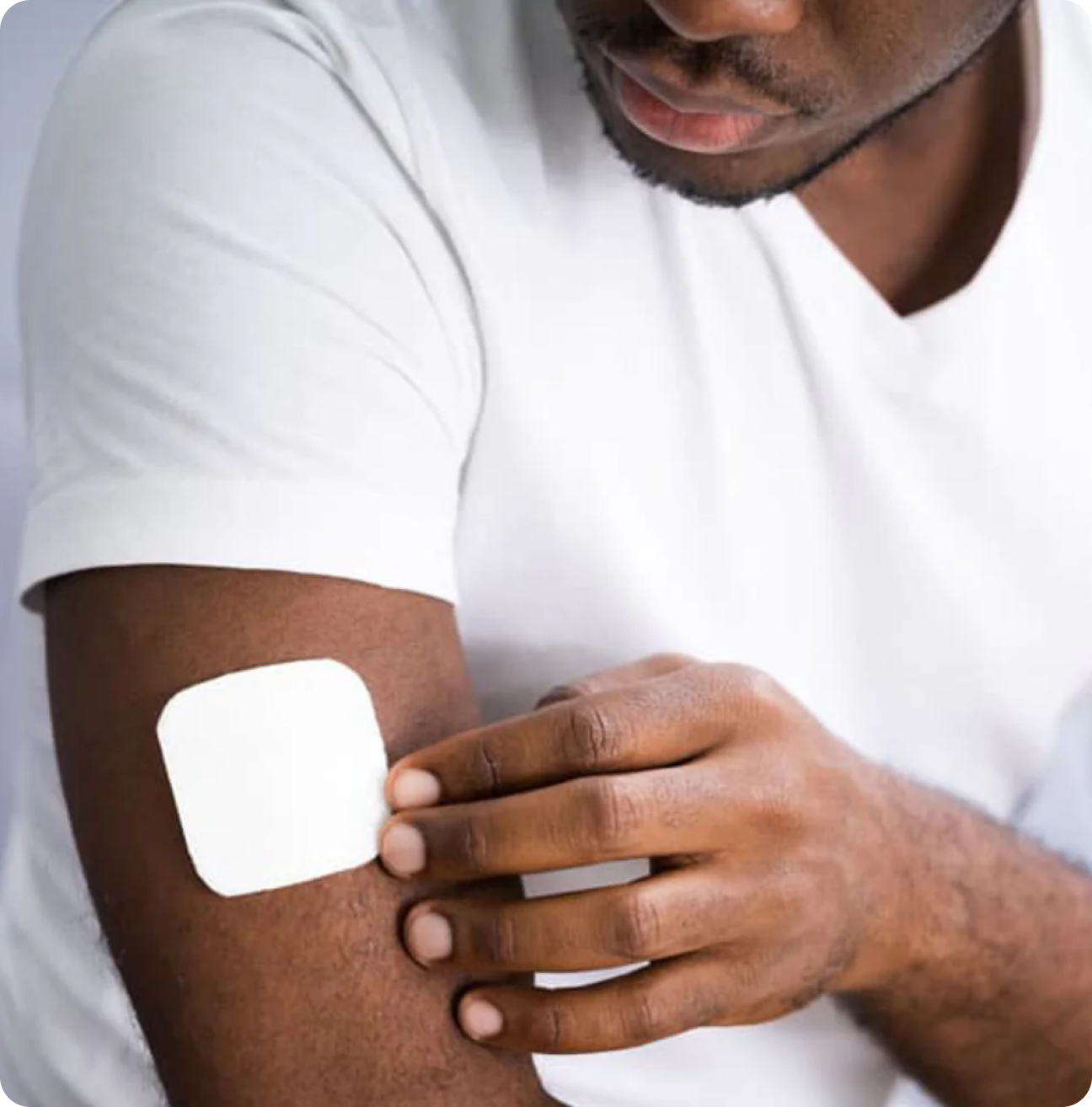
Sensor wear during sleep:
Secure the sensor with Plus Patches:
Apply a patch over the sensor site to prevent dislodgement or damage during physical activities.
Choose sensor placement wisely:
Opt for locations that are less likely to be disturbed during sleep.
Avoid excessive pressure:
Ensure that your sleeping position or bedding does not exert excessive force on the sensor site.